In short, the durability and low maintenance of quartz tubes stem from their exceptional thermal resistance, chemical inertness, and an intrinsically smooth surface. These properties ensure they can withstand extreme process conditions without degrading, while their non-porous nature prevents residue buildup, which simplifies cleaning and minimizes operational downtime.
Quartz is not just durable; it is operationally resilient. Its value comes from a unique combination of high-temperature stability and a non-reactive, smooth surface that resists contamination, making it a reliable and low-maintenance choice for demanding technical applications.

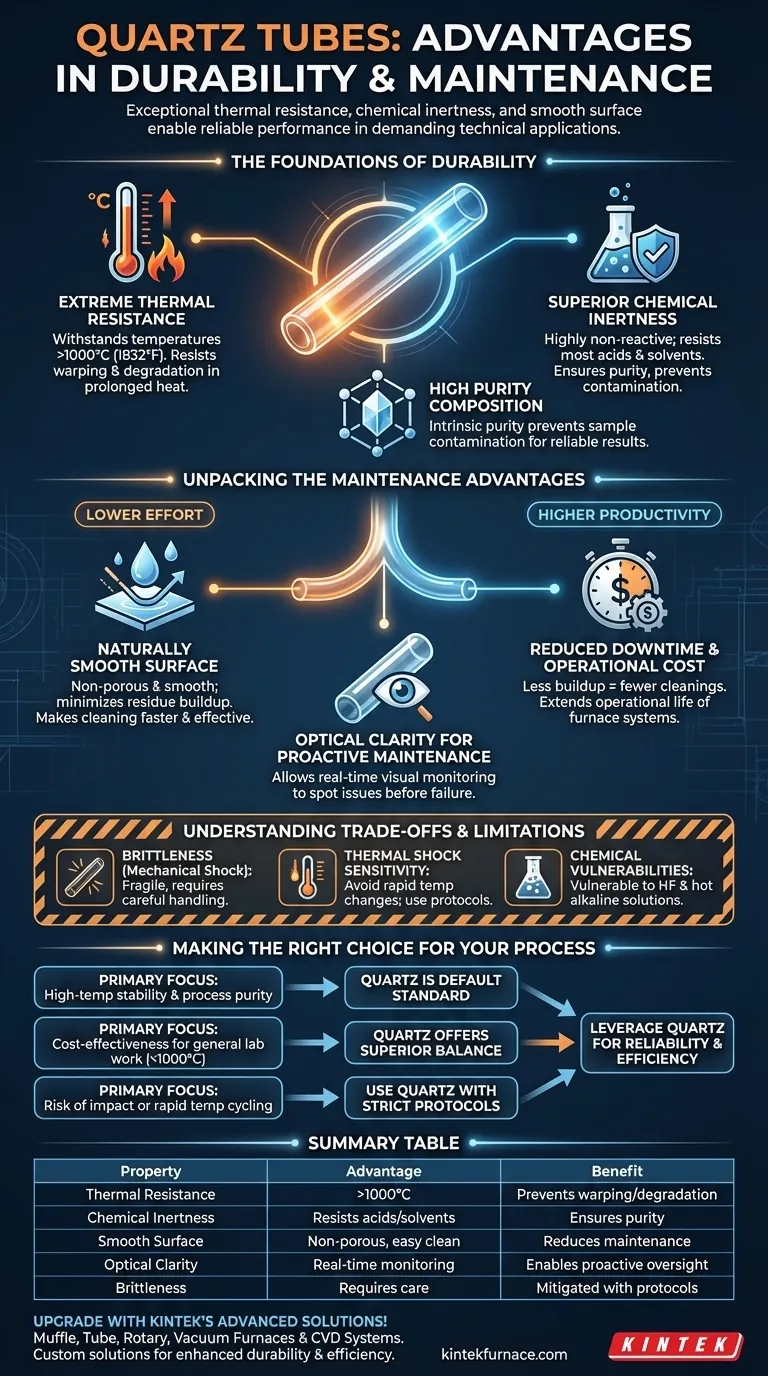
The Foundations of Quartz Tube Durability
The remarkable durability of quartz tubes is not a single feature but the result of several key material properties working in concert. These characteristics make it a default choice for high-stress thermal and chemical environments.
Extreme Thermal Resistance
Quartz tubes are engineered to perform reliably at extreme temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C (1832°F).
Unlike metals or lesser glasses, fused quartz maintains its structural integrity and does not easily warp or degrade under intense, prolonged heat. This makes it ideal for processes like annealing and calcination.
Superior Chemical Inertness
Quartz is highly non-reactive and resistant to corrosion from the vast majority of acids, solvents, and chemical agents.
This chemical stability is critical for two reasons: it protects the tube itself from being etched or weakened, and it ensures the purity of the sample or process inside by not leaching impurities.
High Purity Composition
The material itself, typically fused silica, is exceptionally pure. This intrinsic purity prevents the tube from becoming a source of contamination during sensitive operations.
For applications in semiconductor manufacturing or materials science, this is a form of operational durability, ensuring repeatable and reliable results.
Unpacking the Maintenance Advantages
The low-maintenance nature of quartz is a direct consequence of its physical surface properties and transparency, translating into lower costs and higher productivity.
A Naturally Smooth Surface
The surface of a quartz tube is exceptionally smooth and non-porous at a microscopic level.
This feature significantly minimizes the ability of process residues, byproducts, or contaminants to adhere to the tube walls, making cleaning faster and more effective.
Reduced Downtime and Operational Cost
Because less material builds up on the tube walls, the need for frequent and intensive cleaning is drastically reduced.
This directly results in less downtime for maintenance, lower labor costs, and extended operational life for the tube furnace or reactor system.
Optical Clarity for Proactive Maintenance
The transparency of quartz is a significant operational advantage. It allows for real-time visual monitoring of the process inside.
This clarity also enables operators to inspect the tube's condition and spot potential residue buildup or devitrification (crystallization) before it becomes a critical failure, allowing for proactive rather than reactive maintenance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly advantageous, quartz is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to using it effectively and safely.
Brittleness and Mechanical Shock
Like other ceramics and glasses, quartz is hard but brittle. It has poor resistance to mechanical shock and can fracture or shatter if dropped or struck.
Sensitivity to Thermal Shock
Although it has excellent thermal resistance, rapid and uneven temperature changes (thermal shock) can induce stress and cause it to crack. Proper heating and cooling protocols are essential.
Chemical Vulnerabilities
While broadly inert, quartz can be attacked by a few specific chemicals, most notably hydrofluoric acid and hot alkaline solutions. You must verify chemical compatibility for your specific process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision to use quartz should be based on a clear understanding of your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability and process purity (e.g., semiconductor CVD, advanced material synthesis): Quartz is the default standard, offering an unmatched combination of thermal resistance and inertness.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general lab work (e.g., pyrolysis, annealing below 1000°C): Quartz provides a superior balance of performance and affordability compared to more exotic and expensive ceramic tubes.
- If your primary focus is on processes with risk of physical impact or rapid temperature cycling: You must implement strict handling procedures and controlled heating/cooling ramps to mitigate the risk of breakage from quartz's inherent brittleness.
By understanding these properties, you can confidently leverage quartz tubes to enhance the reliability and efficiency of your high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands temperatures >1000°C | Prevents warping and degradation in extreme heat |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists most acids and solvents | Ensures purity and prevents contamination |
| Smooth Surface | Non-porous and easy to clean | Reduces residue buildup and maintenance frequency |
| Optical Clarity | Allows real-time visual monitoring | Enables proactive maintenance and process oversight |
| Brittleness | Requires careful handling | Mitigated with proper protocols for long-term use |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced quartz tube solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, as well as Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing durability, reducing maintenance, and boosting efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab
- What industrial and research applications are tube furnaces used for? Unlock Precise Thermal Processing Solutions
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the working principle of a vacuum tube furnace? Master Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is the primary function of a vacuum-sealed quartz tube in MnBi2Te4 growth? Ensure High-Purity Crystal Synthesis



















