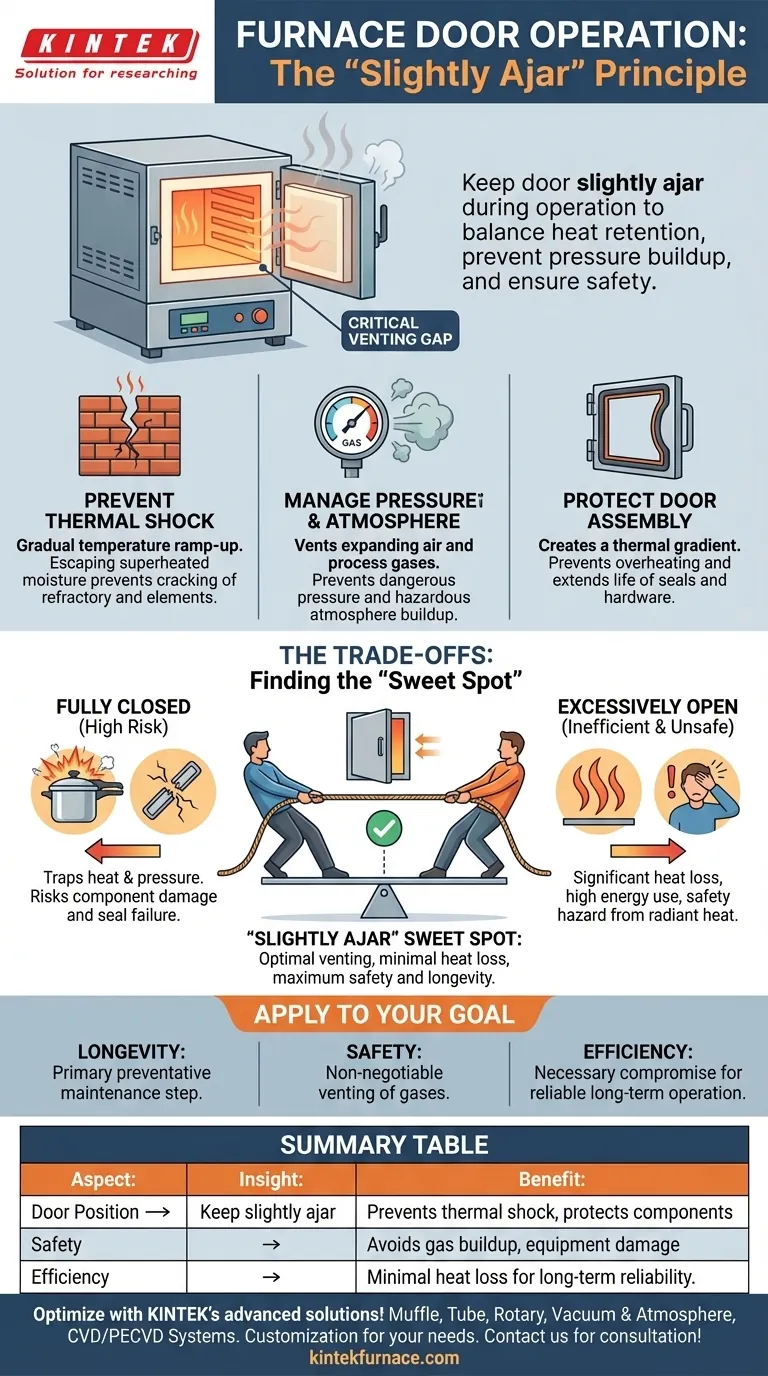
In short, the furnace door should be kept nearly closed but left slightly ajar during operation. This seemingly counterintuitive practice is a critical safety and maintenance procedure designed to protect the furnace's internal components from damage caused by rapid temperature changes and pressure buildup.
The core principle is that a completely sealed furnace chamber during heating is a risk. A small, deliberate opening acts as a crucial vent, balancing heat retention with the long-term health and safety of the equipment.

The Principle: Why a Slight Opening is Critical
Operating a high-temperature furnace is a delicate balance. While your goal is to contain heat, creating a perfectly sealed environment can introduce significant risks to the equipment itself. A small gap in the door is a simple but effective engineering control.
Preventing Thermal Shock
The most significant reason for this practice is to mitigate thermal shock. Refractory materials (the brick or fiber lining) and heating elements are susceptible to cracking when temperatures change too quickly.
Leaving the door slightly ajar allows for a more gradual and controlled temperature ramp-up. It lets superheated moisture and expanding air escape, preventing the kind of rapid thermal and pressure fluctuations that stress and ultimately fracture these expensive components.
Managing Internal Pressure and Atmosphere
As the furnace heats up, the air inside expands dramatically. Without a vent, this creates positive pressure within the chamber, which can strain the door, latches, and seals.
Furthermore, many processes, such as binder burnout or heat-treating oily parts, release gases. A slight opening allows these process gases to vent safely instead of building up inside the chamber, where they could create a hazardous atmosphere or damage the workpiece.
Protecting the Door Assembly
The furnace door itself contains components like gaskets, handles, and observation ports that are not designed to withstand the full, direct internal temperature for prolonged periods.
A small gap helps create a thermal gradient, preventing the outer face and its hardware from reaching extreme temperatures. This simple step extends the life of the door seals and prevents premature failure of its components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The position of the furnace door is a calculated compromise. Deviating from the recommended "slightly ajar" position introduces distinct risks from either extreme.
The Risk of a Fully Closed Door
Keeping the door sealed shut, especially during initial heating, traps expanding air and moisture. This can lead to a rapid pressure increase, potentially damaging the door seals or, in a worst-case scenario, causing components to crack from the combined thermal and physical stress.
The Risk of an Excessively Open Door
Leaving the door wide open results in significant heat loss, making the furnace highly inefficient and dramatically increasing energy consumption. It also creates a potential safety hazard by exposing the operator and the surrounding area to intense radiant heat.
Finding the "Slightly Ajar" Sweet Spot
The ideal opening is typically small—often just a crack. It should be just enough to allow for equalization without causing excessive heat loss. The exact amount depends on the specific furnace model and the process being run, but the principle remains the same.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your operational priority will determine how you view this essential practice.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: View the slightly open door as the single most important preventative maintenance step you can take during operation to avoid costly repairs to heating elements and the furnace lining.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Understand that proper venting is non-negotiable for preventing the buildup of potentially hazardous or combustible gases released from your workpiece.
- If your primary focus is Operational Efficiency: Acknowledge that while a small gap creates minor heat loss, it is a necessary compromise that ensures the furnace can operate safely and reliably for years to come.
Properly managing the furnace door is a simple habit that pays significant dividends in safety, reliability, and equipment lifespan.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Door Position | Keep slightly ajar to vent gases and prevent pressure buildup |
| Primary Benefit | Prevents thermal shock, protects refractory materials and heating elements |
| Safety Consideration | Avoids hazardous gas accumulation and equipment damage |
| Efficiency Trade-off | Minimal heat loss for long-term reliability and energy savings |
Optimize your lab's furnace operations with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with deep customization to meet your unique needs. Ensure safety, efficiency, and durability in your processes—contact us today for a tailored consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control



















