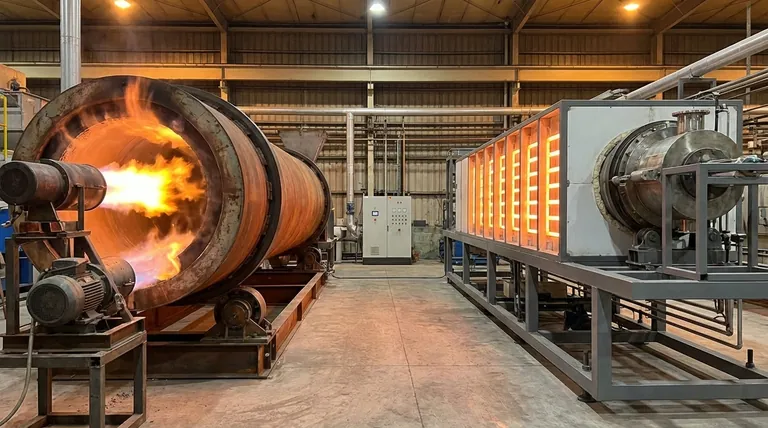
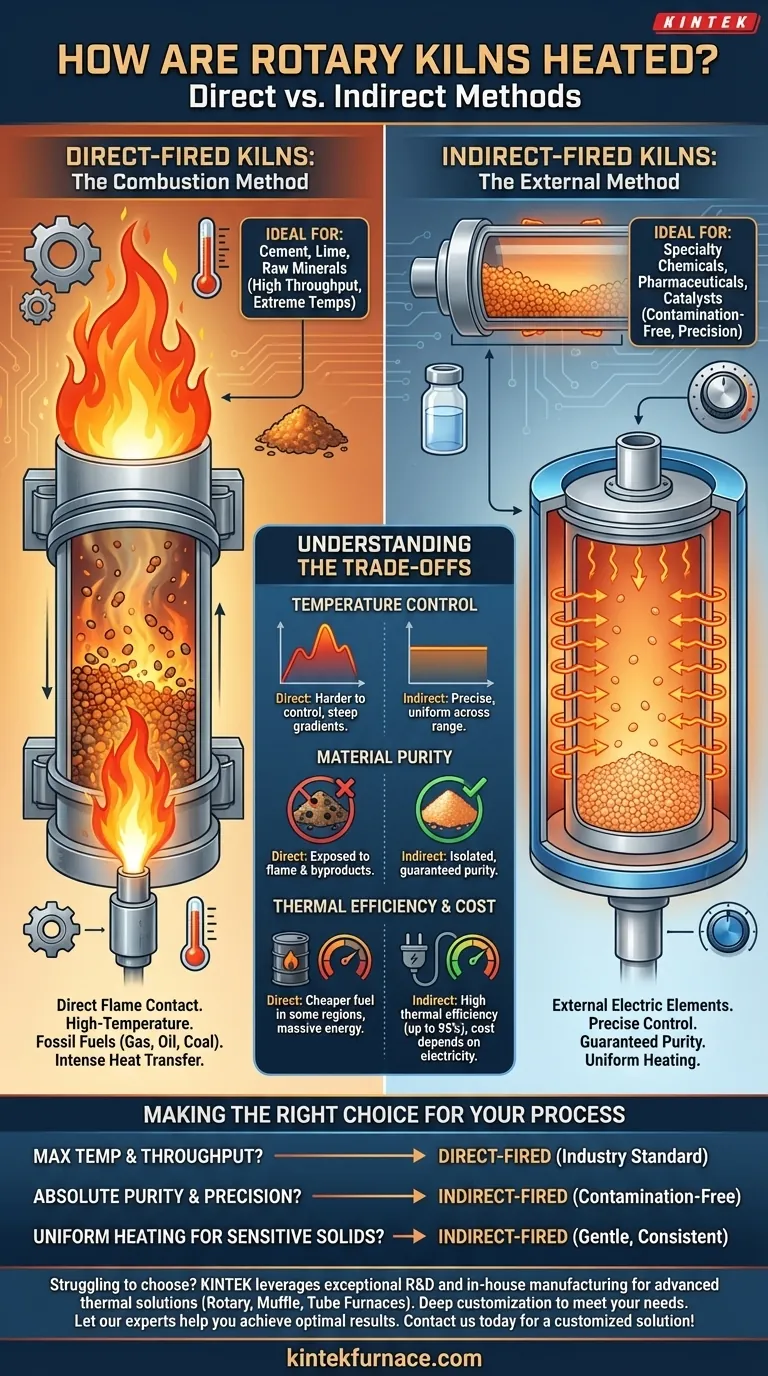
At its core, a rotary kiln is heated using one of two fundamental methods: direct heating or indirect heating. Direct heating involves a burner that introduces a flame directly into the kiln's interior chamber, while indirect heating uses external sources, typically electric elements, to heat the kiln's shell from the outside.
The choice between direct and indirect heating is the most critical decision in kiln design. It is a strategic trade-off between the raw power and high temperatures of direct combustion and the precision, purity, and control offered by indirect electric systems.

The Two Primary Heating Architectures
Understanding how these two methods work reveals their distinct advantages and ideal applications. The core difference lies in whether the material being processed comes into contact with the flame and its byproducts.
Direct-Fired Kilns: The Combustion Method
In a direct-fired system, a powerful burner is positioned at the discharge end of the kiln. It projects a long flame into the rotating cylinder, directly heating both the material and the kiln's internal atmosphere.
This method typically uses combustible fuels like natural gas, heavy oil, or pulverized coal. The intense, direct heat transfer is highly effective for processes that require extremely high temperatures.
Indirect-Fired Kilns: The External Method
Indirect-fired kilns function more like a high-temperature oven. The rotating cylinder, often called a retort, is enclosed within a stationary insulated shell lined with heating elements.
These elements, most commonly electric, heat the outside of the retort. The heat then transfers through the metal shell to the material tumbling inside. Crucially, the material never comes into contact with the heat source or any combustion gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Selecting the right heating system requires a clear understanding of your process goals, as each method presents a different profile of control, cost, and material compatibility.
Temperature Control and Uniformity
Indirect electric heating offers far more precise temperature control across the entire operating range. The heat is applied evenly along the length of the shell, ensuring uniform material processing.
Direct-fired kilns are harder to control with the same level of precision, especially at lower temperatures. The area near the flame will be significantly hotter, creating a steep temperature gradient that can be desirable for some processes but detrimental for others.
Material Purity and Contamination
This is often the deciding factor. Since indirect heating isolates the material from the heat source, it guarantees product purity. This is essential for applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemicals where contamination by combustion byproducts is unacceptable.
In a direct-fired kiln, the material is directly exposed to the flame and flue gases. While this is perfectly acceptable for raw materials like cement or minerals, it makes the method unsuitable for high-purity applications.
Thermal Efficiency and Operating Cost
Modern indirect electric kilns can achieve extremely high thermal efficiency (up to 95%) because the heat is well-contained. However, the overall operating cost is highly dependent on local electricity prices.
Direct-fired systems can be cheaper to run in regions where fossil fuels are less expensive than electricity. Their efficiency can vary, but they are unmatched for delivering massive amounts of thermal energy for large-scale industrial processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines the correct technology. There is no single "best" method; there is only the method that best aligns with your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature and high throughput for raw materials (e.g., cement, lime): A direct-fired combustion kiln is the industry standard and the most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute material purity and precise temperature control (e.g., specialty chemicals, calcining catalysts): An indirect-fired electric kiln is the only option that guarantees a contamination-free process.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating for sensitive granular solids: The consistent and gentle heat of an indirect system will deliver superior results and prevent localized overheating.
Understanding the fundamental difference between direct and indirect heating empowers you to select the right tool for your specific thermal processing goal.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-Fired | High temperatures, direct flame contact, potential for contamination | Cement, lime, raw minerals |
| Indirect-Fired | Precise temperature control, guaranteed material purity, uniform heating | Specialty chemicals, pharmaceuticals, catalysts |
Struggling to choose the right heating method for your rotary kiln process? At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal solutions. Whether you need the raw power of a direct-fired system or the precision and purity of an indirect furnace, our product line—including Rotary, Muffle, and Tube Furnaces—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production requirements. Let our experts help you achieve optimal results. Contact us today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource



















