In material research, the integrity of your experiment is paramount. Quartz tubes are a foundational tool for high-temperature processing primarily because their unique properties create a pristine and stable environment. Their combination of extreme purity, high thermal stability, and chemical inertness ensures that the tube itself does not interfere with or contaminate the sample, allowing for reliable and accurate results.
The choice of a quartz tube is not merely about containing a sample at high temperature. It is a strategic decision to create a chemically and thermally stable environment, ensuring the only variables in your experiment are the ones you intentionally control.
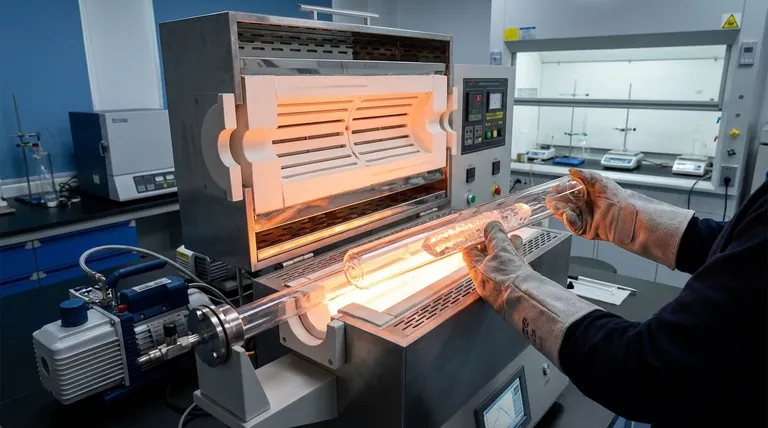

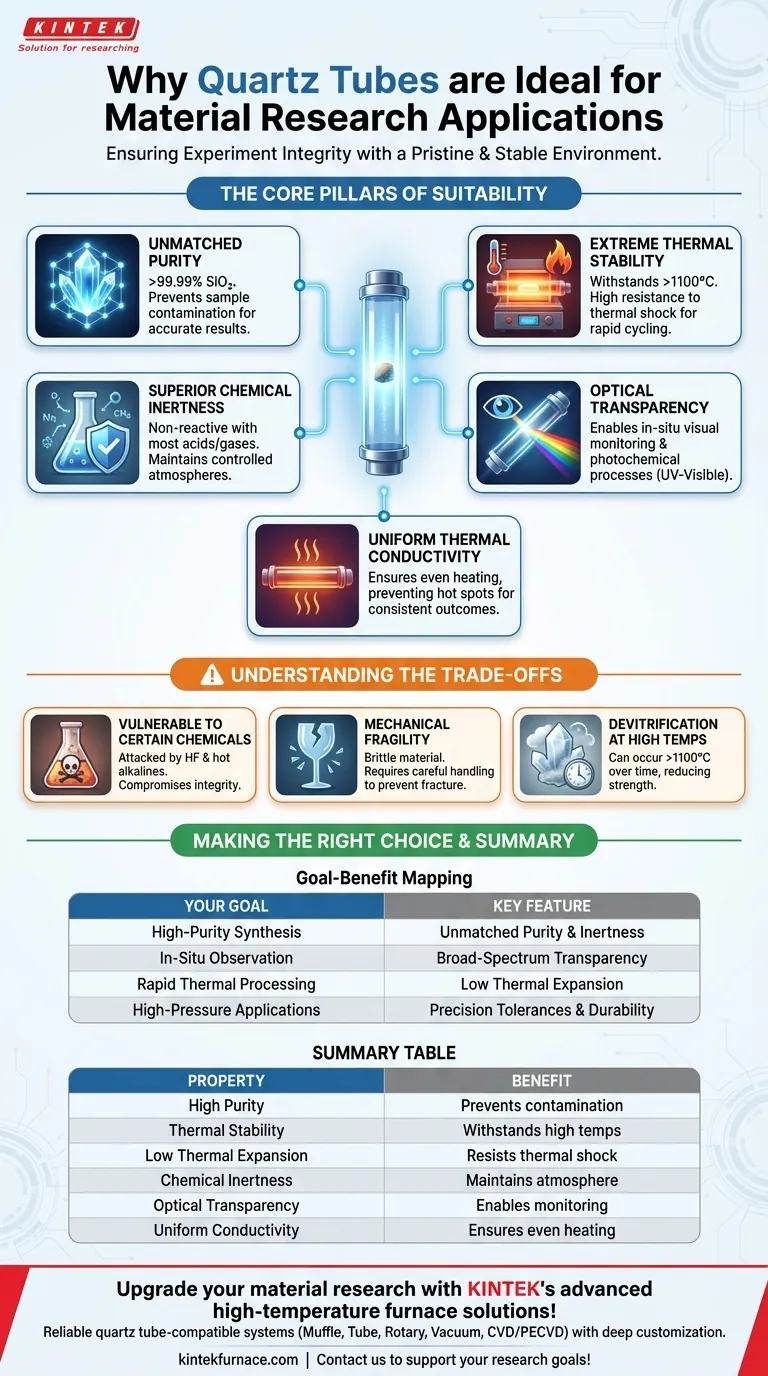
The Core Pillars of Suitability
The widespread use of quartz in research furnaces is due to a specific set of properties that directly address the fundamental requirements of controlled material synthesis and analysis.
Unmatched Purity Prevents Contamination
The most critical feature of a quartz tube is its exceptional purity, often exceeding 99.99% silica (SiO₂).
During high-temperature experiments, materials can become highly reactive. A tube made of a lesser material could leach impurities into your sample, fundamentally altering its composition and invalidating your results. The purity of quartz minimizes this risk.
Extreme Thermal Stability
Quartz tubes exhibit high thermal stability, meaning they can withstand continuous operating temperatures often exceeding 1100°C without deforming or melting.
Furthermore, they possess a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. This makes them highly resistant to thermal shock, allowing for rapid heating and cooling cycles without the risk of cracking, which is essential for processes like rapid thermal annealing.
Superior Chemical Inertness
Quartz is chemically inert to a wide range of materials, including most acids, reactive gases, and chemicals used in material deposition or synthesis.
This inertness is crucial for experiments conducted under a specific atmosphere (e.g., argon, nitrogen, hydrogen). The tube will not react with the process gases, ensuring the sample's environment remains precisely as intended.
Optical Transparency for In-Situ Analysis
Unlike opaque ceramic tubes, quartz is transparent to a broad spectrum of light, including visible and ultraviolet (UV) wavelengths.
This unique property allows researchers to visually monitor the sample during the experiment. It also enables processes that rely on light, such as photochemical reactions or UV-ozone cleaning, to be performed directly within the furnace.
Uniform Thermal Conductivity
Quartz provides excellent and uniform thermal conductivity. This ensures that heat from the furnace elements is transferred evenly throughout the tube and to the sample.
Uniform heating prevents "hot spots," ensuring that the entire sample experiences the same temperature profile. This is critical for consistent phase transformations, crystal growth, and film deposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While quartz is a superior material, it is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these is key to successful experimental design.
Vulnerability to Certain Chemicals
Despite its general inertness, quartz is susceptible to attack by hydrofluoric acid (HF) and hot alkaline substances (e.g., sodium hydroxide). These chemicals will etch and damage the tube, compromising its integrity.
Mechanical Fragility
Like any glass-based material, quartz tubes are brittle. They can fracture from mechanical shock, such as being dropped or improperly secured. Careful handling is always required.
Devitrification at High Temperatures
When held at very high temperatures (typically above 1100°C) for extended periods, quartz can begin to devitrify. This process turns the clear glass into a crystalline, opaque, and more brittle form, reducing its strength and reliability over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Your specific experimental goal will determine which properties of a quartz tube are most important.
- If your primary focus is high-purity synthesis: The unmatched purity and chemical inertness are your most critical factors, preventing sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is in-situ observation or photochemistry: The broad-spectrum optical transparency is the key enabling feature.
- If your primary focus is rapid thermal processing: The low thermal expansion and resulting resistance to thermal shock are essential for tube longevity.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure applications: The precision manufacturing tolerances and inherent durability of quartz make it suitable for maintaining a seal under pressure.
Ultimately, selecting a quartz tube is an investment in experimental control, providing a stable and non-reactive environment essential for generating trustworthy data.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Material Research |
|---|---|
| High Purity (>99.99% SiO₂) | Prevents sample contamination, ensuring accurate results |
| Thermal Stability (up to 1100°C+) | Withstands high temperatures without deformation |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Resists thermal shock for rapid heating/cooling cycles |
| Chemical Inertness | Non-reactive with most acids and gases, maintaining controlled atmospheres |
| Optical Transparency | Enables in-situ visual monitoring and photochemical processes |
| Uniform Thermal Conductivity | Ensures even heating, preventing hot spots for consistent outcomes |
Upgrade your material research with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable quartz tube-compatible systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing purity, control, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















