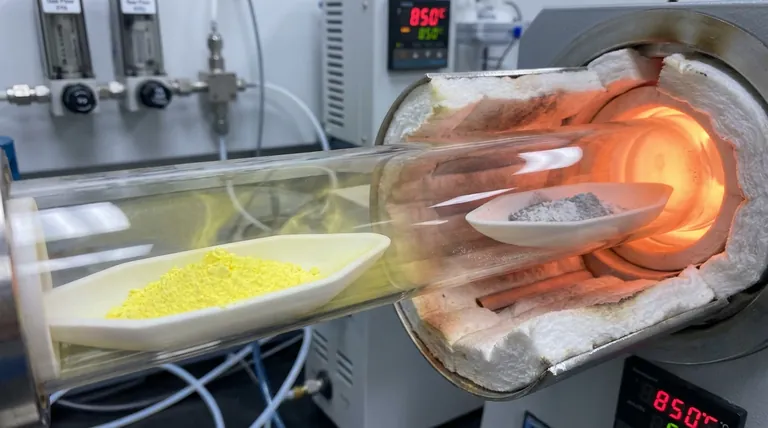
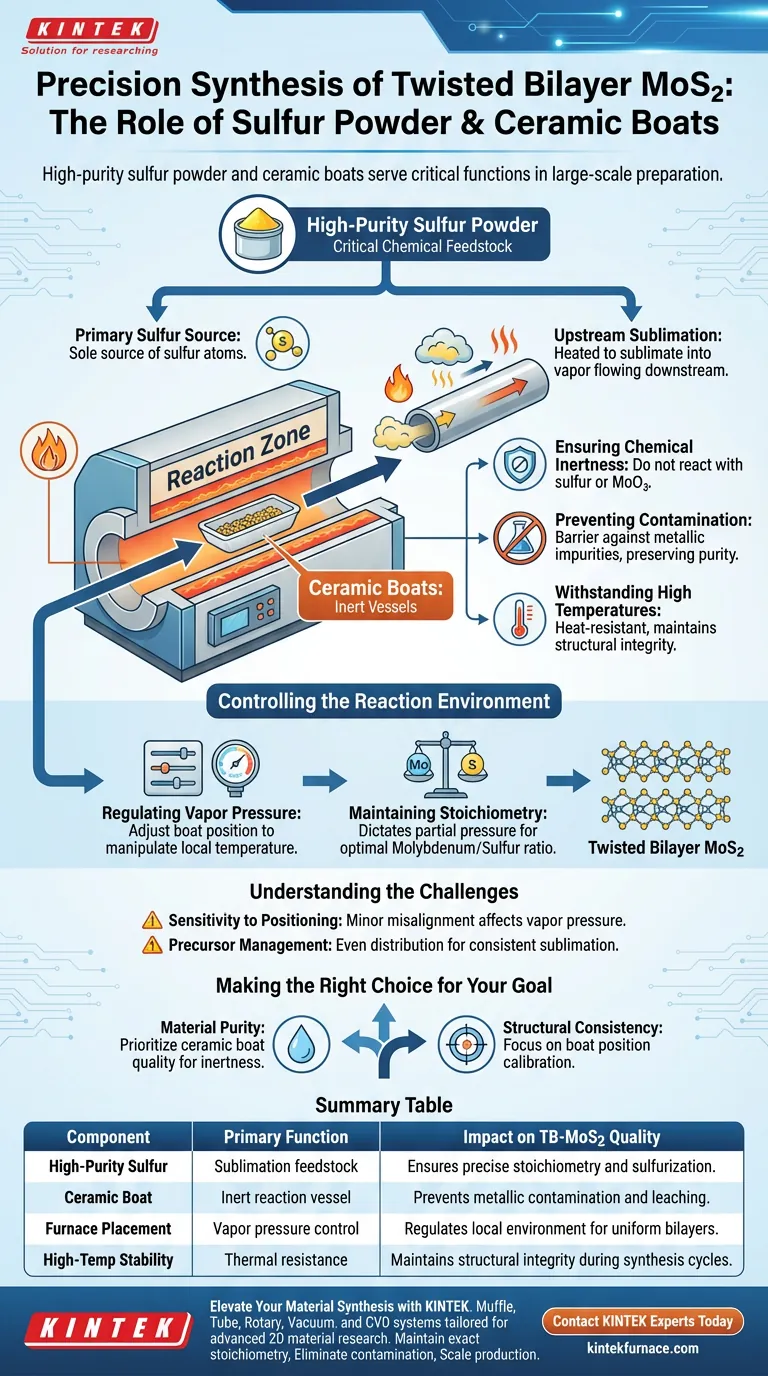
High-purity sulfur powder acts as the critical chemical feedstock for sulfurization, while ceramic boats serve as inert vessels that contain the reactants and enable precise control over the reaction environment. In the synthesis of twisted bilayer molybdenum disulfide (TB-MoS2), these two components work in tandem to ensure the material forms with the correct chemical composition and without external contamination.
The success of large-scale TB-MoS2 preparation relies on the balance between precursor purity and environmental control. Ceramic boats provide the stability needed to manipulate the sulfur vapor pressure, ensuring the stoichiometry of the final material matches the precise requirements of the twisted bilayer structure.

The Role of High-Purity Sulfur Powder
The Primary Sulfur Source
In the synthesis process, high-purity sulfur powder is the foundational raw material. It serves as the sole source of sulfur atoms required to react with molybdenum sources.
Upstream Sublimation
The sulfur powder is placed in the upstream region of the furnace. Here, it is heated until it sublimates, transitioning from a solid powder into a vapor that flows downstream to the reaction zone.
The Function of Ceramic Boats
Ensuring Chemical Inertness
Ceramic boats are chosen specifically for their chemical properties. They are chemically inert, meaning they do not react with the sulfur or the molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) mixture they hold.
Preventing Contamination
A critical function of the ceramic boat is to act as a barrier against impurities. By using ceramic rather than metal containers, the process ensures that no metallic impurities leach into the reaction, preserving the purity of the TB-MoS2.
Withstanding High Temperatures
The synthesis occurs at elevated temperatures. Ceramic boats are heat-resistant, maintaining their structural integrity without degrading or outgassing during the intense heating cycles of the furnace.
Controlling the Reaction Environment
Regulating Vapor Pressure
The ceramic boats are not static containers; they are tools for process control. By adjusting the physical position of the boats within the furnace tube, operators can precisely manipulate the local temperature they are exposed to.
Maintaining Stoichiometry
This positioning directly dictates the partial pressure of the sulfur vapor at the reaction zone. Controlling this pressure is essential for maintaining the correct stoichiometry, ensuring the ratio of Molybdenum to Sulfur remains optimal for forming high-quality twisted bilayers.
Understanding the Challenges
Sensitivity to Positioning
While ceramic boats allow for control, the process is highly sensitive to their placement. Because the thermal gradient in a furnace can be steep, a minor misalignment of the boat can result in significant deviations in sulfur vapor pressure.
Precursor Management
The use of powder requires careful handling. Ensuring the sulfur powder is evenly distributed within the boat is necessary to achieve consistent sublimation rates throughout the large-scale preparation process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving high-quality TB-MoS2 requires treating these components as part of an interconnected system rather than isolated variables.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Prioritize the quality of your ceramic boats to ensure absolute inertness, eliminating the risk of metallic contamination.
- If your primary focus is structural consistency: Focus on the precise calibration of the boat's position within the furnace to lock in the exact sulfur vapor pressure required for stoichiometric balance.
Precision in the physical setup translates directly to precision in the atomic structure.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Impact on TB-MoS2 Quality |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Sulfur | Sublimation feedstock | Ensures precise stoichiometry and sulfurization. |
| Ceramic Boat | Inert reaction vessel | Prevents metallic contamination and leaching. |
| Furnace Placement | Vapor pressure control | Regulates the local environment for uniform bilayers. |
| High-Temp Stability | Thermal resistance | Maintains structural integrity during synthesis cycles. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in large-scale TB-MoS2 preparation demands hardware that can withstand extreme thermal gradients while maintaining absolute purity. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for advanced 2D material research.
Our customizable laboratory high-temperature furnaces empower you to:
- Maintain exact stoichiometry through superior temperature uniformity.
- Eliminate contamination with specialized inert vessel compatibility.
- Scale production with reliable, repeatable heating cycles.
Whether you need standard lab equipment or a bespoke solution for unique material growth, our team is ready to support your technical requirements.
Contact KINTEK Experts Today to optimize your synthesis process!
Visual Guide
References
- Manzhang Xu, Wei Huang. Reconfiguring nucleation for CVD growth of twisted bilayer MoS2 with a wide range of twist angles. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44598-w
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucible required for the melting of nickel-based superalloys?
- What function does a vacuum pump perform in simulated vacuum refining? Optimize Aluminum Alloy Purity & Defect Analysis
- How does the selection of a ceramic crucible contribute to the preparation of biomass carbon catalysts? Maximize Purity
- What is the function of laboratory pellet presses and steel dies? Maximize Reaction Kinetics in Oxide Processing
- Why is the use of casting flux necessary during the melting of aluminum-based alloys? Protect Your Chemical Integrity
- What critical functions do high-purity graphite molds perform? The Engine of SPS for High-Entropy Ceramics
- How does heating equipment with magnetic stirring contribute to Fe3O4 synthesis? Achieve Precise Nanoparticle Control
- What is the purpose of using an insulating layer in CCCM thermal conductivity tests? Ensuring 1D Heat Flow Accuracy

