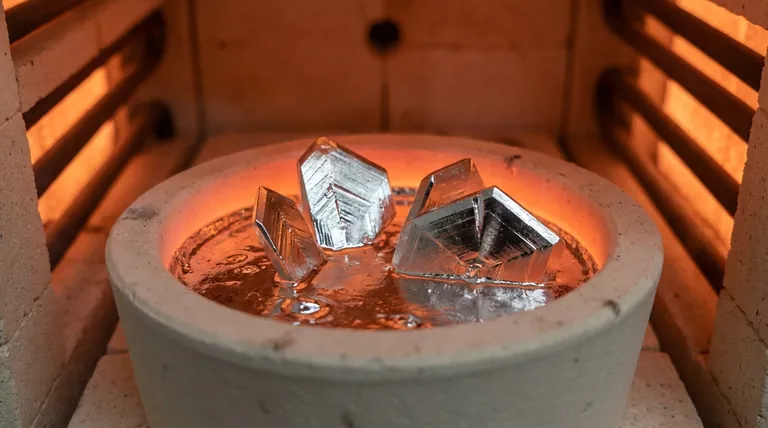
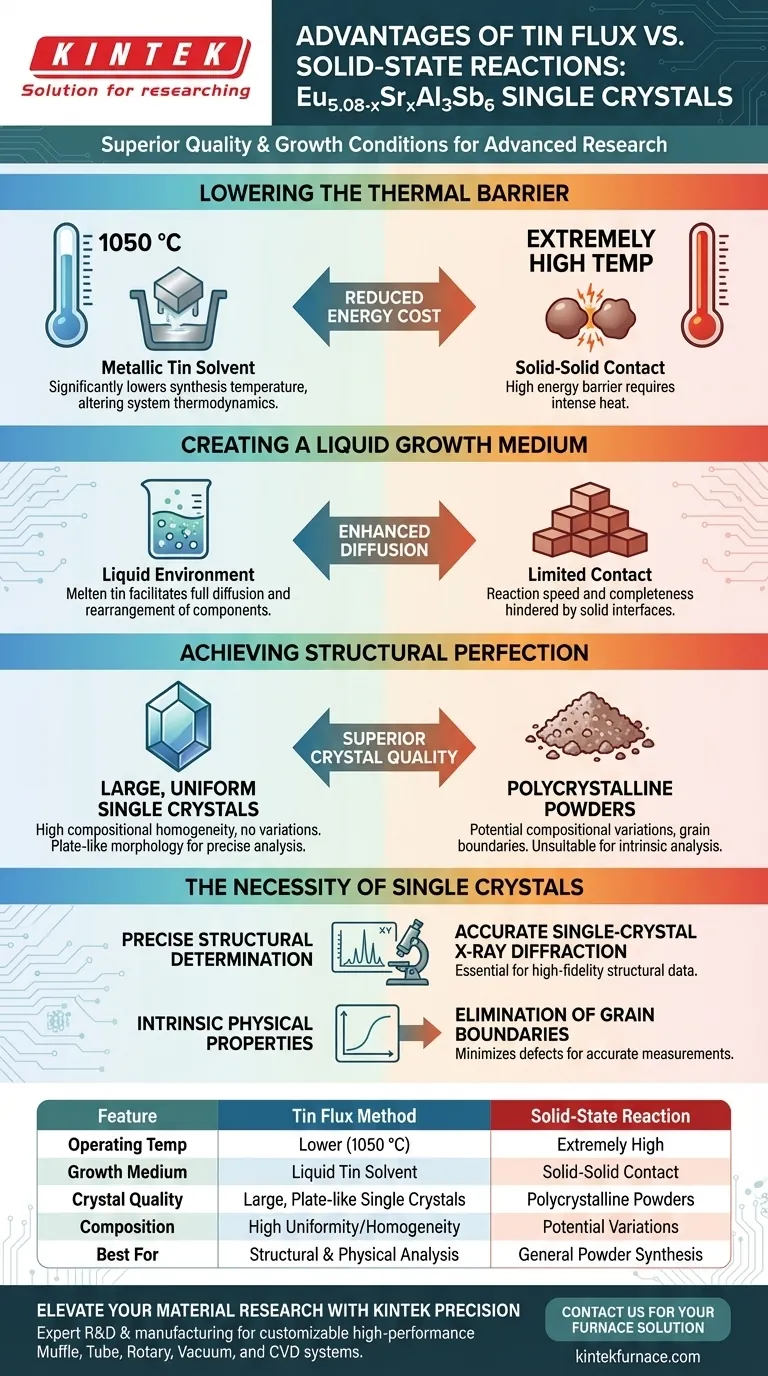
The tin flux method offers a decisive advantage in crystal quality and growth conditions compared to solid-state reactions. By utilizing metallic tin as a solvent, this approach significantly lowers the required synthesis temperature to 1050 °C while facilitating the growth of large, compositionally uniform single crystals essential for advanced characterization.
The liquid solvent environment of the tin flux method solves the diffusion limitations inherent in solid-state reactions, enabling the formation of high-quality, large plate-like crystals required for precise physical and structural analysis.

The Role of Temperature and Solvents
Lowering the Thermal Barrier
In standard solid-state reactions, overcoming the energy barrier for reaction often requires extremely high temperatures.
The tin flux method utilizes metallic tin as a solvent to fundamentally alter the thermodynamics of the system.
This solvent significantly lowers the melting point of the reaction components, allowing synthesis to proceed at a relatively low temperature of 1050 °C.
Creating a Liquid Growth Medium
Solid-state reactions rely on contact between solid particles, which can limit reaction speed and completeness.
The metallic tin flux provides a liquid environment during the heating phase.
This facilitates the full diffusion and rearrangement of components, ensuring the reaction proceeds to completion more effectively than in a solid-state mixture.
Achieving Structural Perfection
Compositional Uniformity
Homogeneity is critical for studying complex solid solutions like Eu5.08-xSrxAl3Sb6.
The fluid nature of the flux method promotes a uniform distribution of elements throughout the crystal lattice.
This results in high-quality single crystals that lack the compositional variations often found in samples prepared via solid-state sintering.
Morphology and Size
Physical characterization techniques often require samples of specific dimensions.
The tin flux method promotes the growth of large, plate-like single crystals.
This specific morphology is a direct result of the enhanced atomic mobility provided by the molten tin solvent.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Necessity of Single Crystals
While solid-state reactions are useful for producing polycrystalline powders, they generally fail to yield single crystals suitable for intrinsic analysis.
The trade-off here is one of preparation complexity versus data fidelity.
Characterization Requirements
If the goal is accurate single-crystal X-ray diffraction, a powder sample is insufficient.
Similarly, precise physical property characterization requires the elimination of grain boundaries.
Therefore, the tin flux method is not merely advantageous but essential when the end goal is high-fidelity structural data.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the appropriate synthesis route for Eu5.08-xSrxAl3Sb6, evaluate your characterization needs.
- If your primary focus is precise structural determination: Use the tin flux method to obtain large single crystals necessary for accurate single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
- If your primary focus is intrinsic physical properties: Rely on the tin flux method to ensure compositional uniformity and minimize defects that could skew physical property measurements.
The tin flux method remains the definitive standard for producing research-grade single crystals of this solid solution.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tin Flux Method | Solid-State Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temp | Lower (1050 °C) | Extremely High |
| Growth Medium | Liquid Tin Solvent | Solid-Solid Contact |
| Crystal Quality | Large, Plate-like Single Crystals | Polycrystalline Powders |
| Composition | High Uniformity/Homogeneity | Potential Variations |
| Best For | Structural & Physical Analysis | General Powder Synthesis |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Are you looking to optimize your crystal growth or high-temperature synthesis? Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Whether you are performing tin flux growth or complex solid-state reactions, our equipment provides the thermal stability and precision required for breakthrough results. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
References
- Luis Garay, Susan M. Kauzlarich. Interplay of Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties of the Eu<sub>5.08-x</sub>Sr<sub><i>x</i></sub>Al<sub>3</sub>Sb<sub>6</sub> Solid Solution. DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c04927
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a Zinc Oxide (ZnO) catalyst affect PET pyrolysis? Optimize Yields & Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a vacuum oven for Mo-based catalyst precursors? Ensure Purity & Pore Integrity
- What is the purpose of the constant-temperature circulation phase? Ensure Moso Bamboo Integrity with KINTEK Solutions
- Why is staged temperature control required in industrial air drying ovens for carbon nanofibers? Key Safety Insights
- Why is a vacuum drying oven necessary for activated carbon? Ensure Accurate BET and Pore Size Analysis
- What is the function of a gas-phase catalytic reaction system? Evaluate Carbon-Metal Nanocomposites with Precision
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven utilized for ZnO-FL drying? Preserving Delicate Nanoparticle Morphologies
- What is the specific function of laboratory electric heating devices in solid-state hydrogen storage? Optimize Thermal Management


