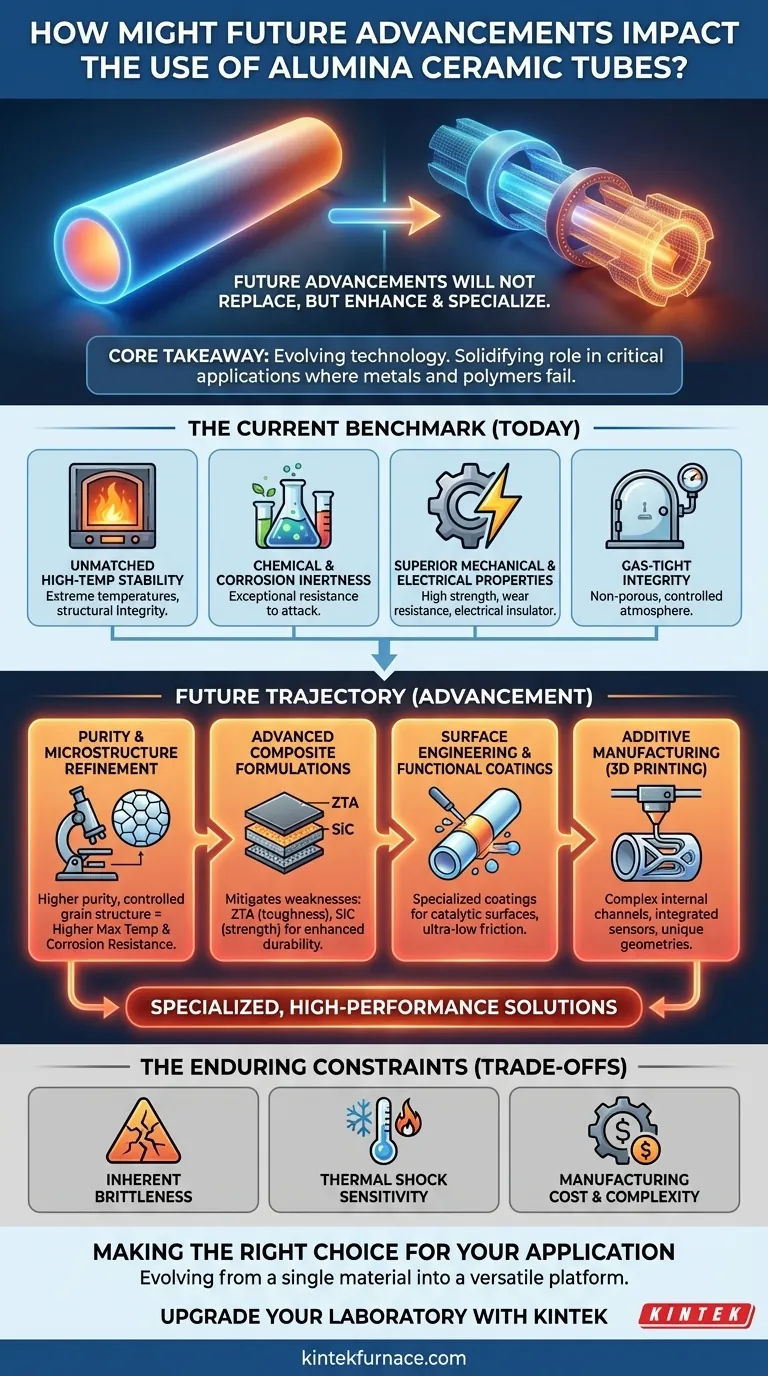
In short, future advancements will not replace alumina ceramic tubes but will instead enhance their performance and specialize their function. Progress in material science and preparation technology is set to improve their thermal, mechanical, and chemical resistance, expanding their use into even more demanding high-temperature and extreme industrial environments.
The core takeaway is that alumina ceramics are an evolving technology. Instead of becoming obsolete, they are becoming more specialized through composite materials and advanced manufacturing, solidifying their role as a critical material for applications where metals and polymers fail.

The Current Benchmark: Why Alumina Tubes are Critical Today
To understand the future, we must first appreciate the present. Alumina (Al₂O₃) ceramic tubes are the default choice in many industries for a clear set of reasons.
Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
Alumina maintains its structural integrity and strength at extreme temperatures where most metals would weaken or melt. This makes it indispensable for components in high-temperature vacuum furnaces, muffle furnaces, and kilns.
Chemical and Corrosion Inertness
These tubes exhibit exceptional resistance to corrosion and chemical attack. This property is vital in harsh processes, such as those found in the float glass and aluminum trichloride industries, where reactive materials are common.
Superior Mechanical and Electrical Properties
Alumina possesses high compressive strength and excellent wear and abrasion resistance. Critically, it is an outstanding electrical insulator (dielectric), making it perfect for protecting heating elements, thermocouples, and other electrical lead-outs in high-heat zones.
Gas-Tight Integrity
High-purity alumina tubes can be manufactured to be non-porous and gas-tight. This is crucial for creating a stable vacuum or a controlled protective atmosphere in laboratory analysis, sintering, and advanced material processing.
Future Trajectory: Key Areas of Advancement
The "progress in material science" mentioned in research is not a vague concept. It translates into specific, tangible improvements that will redefine the capabilities of alumina tubes.
Purity and Microstructure Refinement
The single biggest performance gain comes from improving material purity and controlling the grain structure (microstructure) of the ceramic. Future manufacturing will yield higher-purity alumina with near-zero contamination, directly increasing the maximum service temperature and corrosion resistance.
Advanced Composite Formulations
The future of alumina is not just pure alumina. By creating composites, we can mitigate its primary weaknesses.
- Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA): Adding zirconia particles dramatically improves fracture toughness and thermal shock resistance.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) Reinforcement: Incorporating SiC whiskers or particles can further enhance hardness, strength, and thermal conductivity.
Surface Engineering and Functional Coatings
A simple tube can be transformed into an active component. Future advancements will focus on applying specialized coatings that bestow new properties, such as catalytic surfaces for chemical reactors or ultra-low friction coatings for high-wear applications.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Current methods allow for custom lengths and diameters, but 3D printing of ceramics is the next frontier. This will enable the creation of tubes with incredibly complex internal channels, integrated sensors, or unique geometries that are impossible to produce with traditional extrusion or casting.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Enduring Constraints
Even with future advancements, alumina ceramics will operate within a set of fundamental limitations. Acknowledging these is key to proper application.
Inherent Brittleness
This is the classic Achilles' heel of ceramics. While composites improve toughness, alumina will never have the ductility of metal. It is notch-sensitive and can fail catastrophically under certain impact or tensile loads.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
Alumina has low thermal expansion, which helps with thermal shock, but rapid temperature changes can still cause cracking. Advanced composites will mitigate this, but it will always remain a primary design consideration compared to many alloys.
Manufacturing Cost and Complexity
The processes required to create high-purity, dense, or composite alumina components are energy-intensive and complex. As performance specifications increase, so will the cost, making it a material chosen for necessity, not economy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these future trends to guide your material selection for extreme-environment projects.
- If your primary focus is pushing temperature and purity limits: Source tubes made with the latest refinement technologies, specifying the highest possible alumina purity for your application.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability and thermal shock: Look beyond pure alumina and investigate advanced composites like Zirconia Toughened Alumina (ZTA).
- If your primary focus is complex geometries or rapid prototyping: Monitor the development of ceramic additive manufacturing for creating integrated, monolithic components.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective reliability in standard applications: Current high-purity alumina tubes remain an excellent, proven, and highly capable choice.
Ultimately, the future of alumina ceramic tubes lies in their evolution from a single material into a versatile platform for specialized, high-performance solutions.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Current State | Future Advancements |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Stability | High-temperature stability up to extreme limits | Higher purity increases max service temperature |
| Mechanical Properties | High compressive strength, but brittle | Composites like ZTA enhance toughness and shock resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent corrosion inertness | Improved purity and coatings boost resistance |
| Manufacturing | Custom lengths/diameters via extrusion | 3D printing enables complex geometries and integrated features |
Upgrade Your Laboratory with Custom High-Temperature Solutions from KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need enhanced alumina ceramic tubes for extreme environments or specialized furnace systems, we deliver reliable, high-performance equipment tailored to your needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions



















