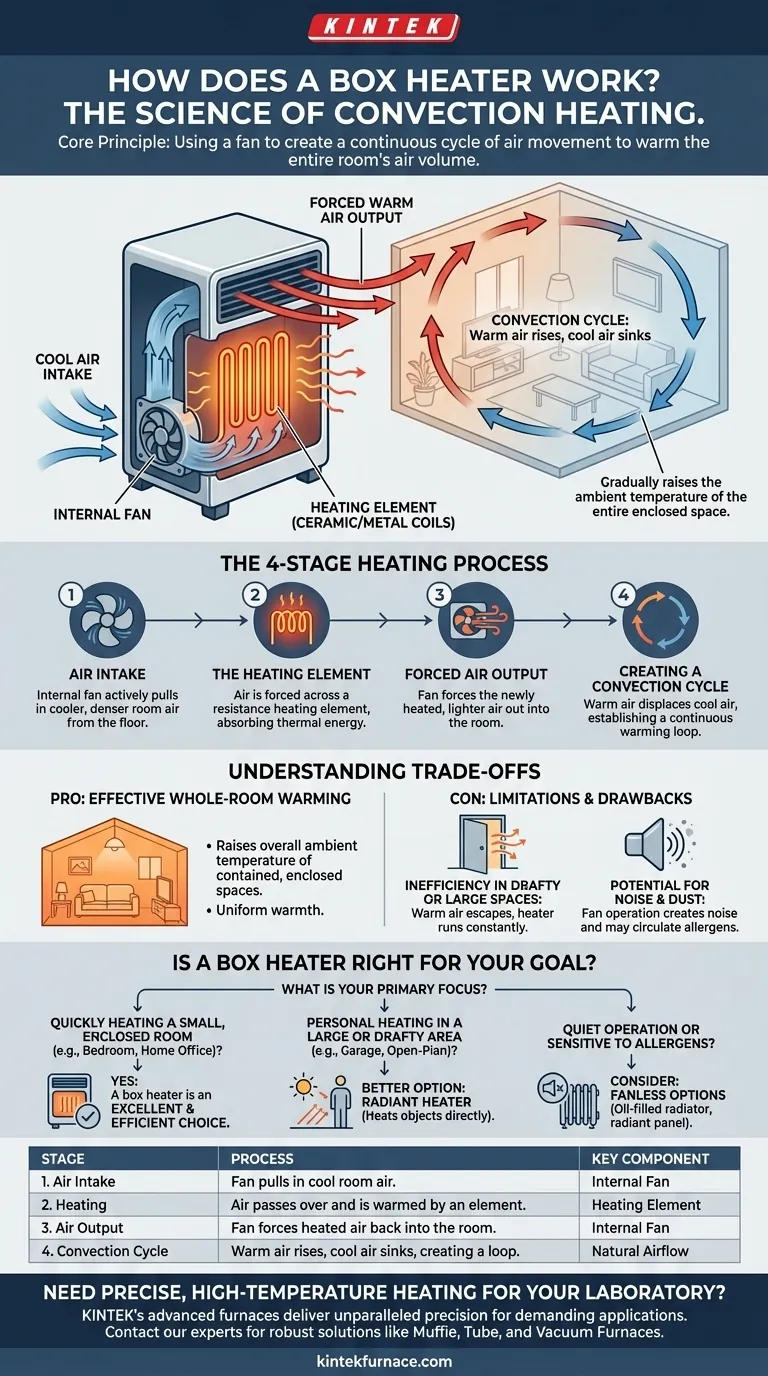
At its core, a box heater works by using a fan to create a continuous cycle of air movement. It pulls cool air from the room, passes it across an internal electric heating element to warm it, and then pushes that heated air back out, creating a convection current that gradually raises the entire room's temperature.
A box heater is a type of convection heater. Its design is not meant to heat you directly like the sun, but rather to heat the volume of air in an enclosed space, making it ideal for raising the ambient temperature of an entire room.

The Step-by-Step Heating Process
To truly understand a box heater's function, we need to look at it as a simple, four-stage system. Each stage plays a critical role in the overall process of warming your space.
Stage 1: Air Intake
The process begins with the internal fan. It actively pulls in cooler, denser air, which naturally settles near the floor of your room.
Stage 2: The Heating Element
This captured air is immediately forced across a heating element. This component, typically made of ceramic plates or metal coils, converts electrical energy into heat through resistance. The air absorbs this thermal energy as it passes over the hot surfaces.
Stage 3: Forced Air Output
The same fan that pulled the cool air in now forces the newly heated, lighter air out of the front of the unit. This creates a tangible flow of warm air you can feel.
Stage 4: Creating a Convection Cycle
This is the key to how a box heater warms an entire room. The expelled hot air rises towards the ceiling, displacing the cooler air and pushing it down towards the floor, where it is then pulled into the heater again. This continuous loop, known as a convection cycle, circulates and warms all the air in the room over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Convection Heating
While effective, the convection method used by box heaters comes with a specific set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding them is critical to knowing if it's the right tool for your needs.
Pro: Effective Whole-Room Warming
Because they heat the air itself, box heaters are excellent at raising the overall ambient temperature of a contained, enclosed space. They create a uniform warmth throughout the room rather than just a single hot spot.
Con: Inefficiency in Drafty or Large Spaces
The primary weakness of a convection heater is its reliance on heating a contained volume of air. If a room has drafts, is very large, or has high ceilings, the warm air can escape or dissipate, forcing the heater to run constantly and inefficiently.
Con: Potential for Noise and Dust Circulation
The fan is essential to a box heater's operation, but it generates noise. Furthermore, by circulating all the air in a room, the fan can also kick up and distribute dust, pet dander, and other allergens, which can be a concern for sensitive individuals.
Is a Box Heater Right for Your Goal?
Choosing the right heater means matching the technology to the environment. Based on the convection principle, a box heater is a specialized tool.
- If your primary focus is quickly heating a small, enclosed room (like a bedroom or home office): A box heater is an excellent and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is personal heating in a large or drafty area (like a garage or open-plan living space): You will be better served by a radiant heater, which heats objects and people directly rather than the air.
- If your primary focus is quiet operation or you are sensitive to airborne allergens: Consider fanless options like an oil-filled radiator or a radiant panel heater.
Understanding this core mechanism of air circulation empowers you to select the right heating tool for your specific environment.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Process | Key Component |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Air Intake | Fan pulls in cool room air. | Internal Fan |
| 2. Heating | Air passes over and is warmed by an element. | Heating Element (ceramic/metal) |
| 3. Air Output | Fan forces the heated air back into the room. | Internal Fan |
| 4. Convection Cycle | Warm air rises, cool air sinks, creating a continuous warming loop. | Natural Airflow |
Need Precise, High-Temperature Heating for Your Laboratory?
While a standard box heater warms a room, KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces deliver unparalleled precision and control for your most demanding applications. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with robust solutions like Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum Furnaces, all with deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements.
Let's discuss your specific thermal processing needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan










