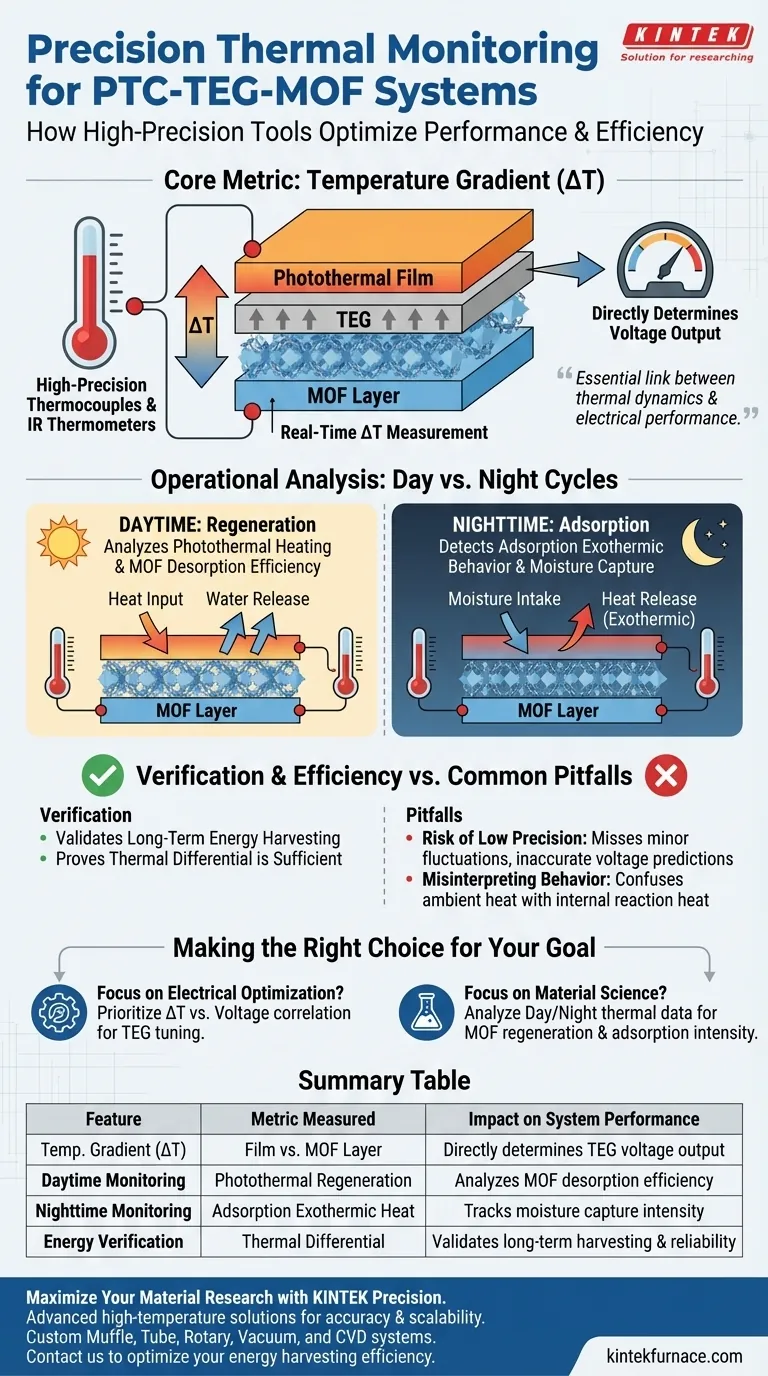
High-precision thermocouples and infrared thermometers serve a critical diagnostic function by measuring the real-time temperature gradient ($\Delta T$) between the system's photothermal film and the metal-organic framework (MOF) layer. This specific thermal data is the direct indicator of the Thermoelectric Generator's (TEG) voltage output capability, acting as the primary metric for system performance.
These measurement tools provide the essential link between thermal dynamics and electrical performance, allowing researchers to correlate physical changes in MOF materials directly with the system's energy harvesting efficiency.
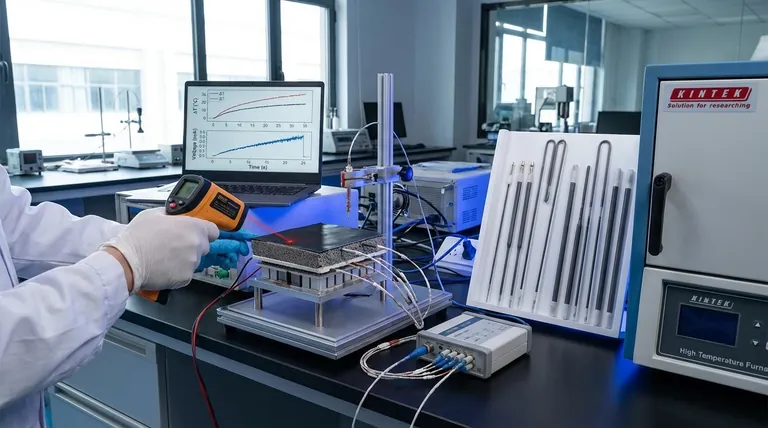

The Core Metric: Temperature Gradient ($\Delta T$)
Real-Time Monitoring
The primary role of these instruments is to capture the temperature difference between the photothermal film and the MOF layer.
This monitoring must occur in real-time to accurately reflect the dynamic state of the system.
Determining Voltage Output
The data collected is not merely for thermal observation; it determines the electrical potential of the system.
The magnitude of the temperature gradient ($\Delta T$) directly dictates the voltage output level generated by the TEG component.
Operational Analysis: Day vs. Night Cycles
Analyzing Daytime Regeneration
During daylight hours, the system relies on the thermal regeneration of MOF materials.
High-precision sensors provide the data necessary to analyze how effectively the MOF layer heats up and regenerates (desorbs water) under photothermal influence.
Analyzing Nighttime Adsorption
At night, the system's behavior shifts to moisture capture.
The sensors are used to detect adsorption exothermic behavior, monitoring the heat released as the MOF materials adsorb water from the air, which contributes to the temperature gradient.
Verification and Efficiency
Validating Energy Harvesting
Beyond instant readings, these tools are essential for verifying the long-term energy harvesting efficiency of the PTC-TEG-MOF system.
They provide the empirical basis required to prove that the thermal differential is sufficient to drive the TEG effectively.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Low Precision
The relationship between the MOF layer's behavior and the TEG's output can be subtle.
Using standard-precision tools may fail to detect minor fluctuations in the temperature gradient, leading to inaccurate predictions of voltage output.
Misinterpreting Thermal Behavior
Without real-time data, it is difficult to distinguish between external ambient heating and internal reaction heat (exothermic adsorption).
Precise monitoring is required to attribute temperature changes correctly to the MOF's adsorption or regeneration processes, rather than environmental noise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your monitoring setup, align your data analysis with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Electrical Optimization: Prioritize the correlation between $\Delta T$ magnitude and voltage output to tune the TEG's operating range.
- If your primary focus is Material Science: Focus on the day/night thermal data to analyze the regeneration efficiency and exothermic intensity of the MOF layer.
High-precision thermal monitoring transforms raw temperature data into a clear roadmap for optimizing both material behavior and electrical generation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Metric Measured | Impact on System Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Gradient (ΔT) | Film vs. MOF Layer | Directly determines TEG voltage output levels |
| Daytime Monitoring | Photothermal Regeneration | Analyzes MOF desorption and thermal regeneration efficiency |
| Nighttime Monitoring | Adsorption Exothermic Heat | Tracks moisture capture intensity through heat release |
| Energy Verification | Thermal Differential | Validates long-term harvesting and system reliability |
Maximize Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Precise thermal management is the foundation of high-performance PTC-TEG-MOF research. KINTEK empowers scientists and engineers with advanced high-temperature laboratory solutions designed for accuracy and scalability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to meet the unique thermal processing needs of your MOF materials and thermoelectric devices.
Ready to optimize your energy harvesting efficiency? Contact us today to discuss how our custom furnace systems can support your next breakthrough.
Visual Guide
References
- Niansi Li, Qiliang Wang. A Multifunctional Photothermal Catalyst Enabling Full‐Day Sustainable Power and Indoor Air Quality Control. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202505059
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
People Also Ask
- What safety features do ceramic infrared heaters include? Ensure Safe, Efficient Heating for Your Space
- What role do heating elements play in a sintering furnace? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Superior Sintering
- What is the role of resistivity in heating elements? Unlock Efficient Heat Generation for Your Applications
- In which industrial applications are SiC heating elements particularly useful? Essential for High-Temp Metal, Glass, and Semiconductor Processes
- What types of silicon carbide heating elements are available? Choose the Right Shape for Your High-Temp Needs
- What precautions should be taken during the installation of heating elements? Ensure Longevity and Performance
- Why are ceramic infrared heaters considered environmentally friendly? Discover Clean, Efficient Heating Solutions
- How is power requirement determined for heaters? Calculate Energy Needs for Efficient Heating
