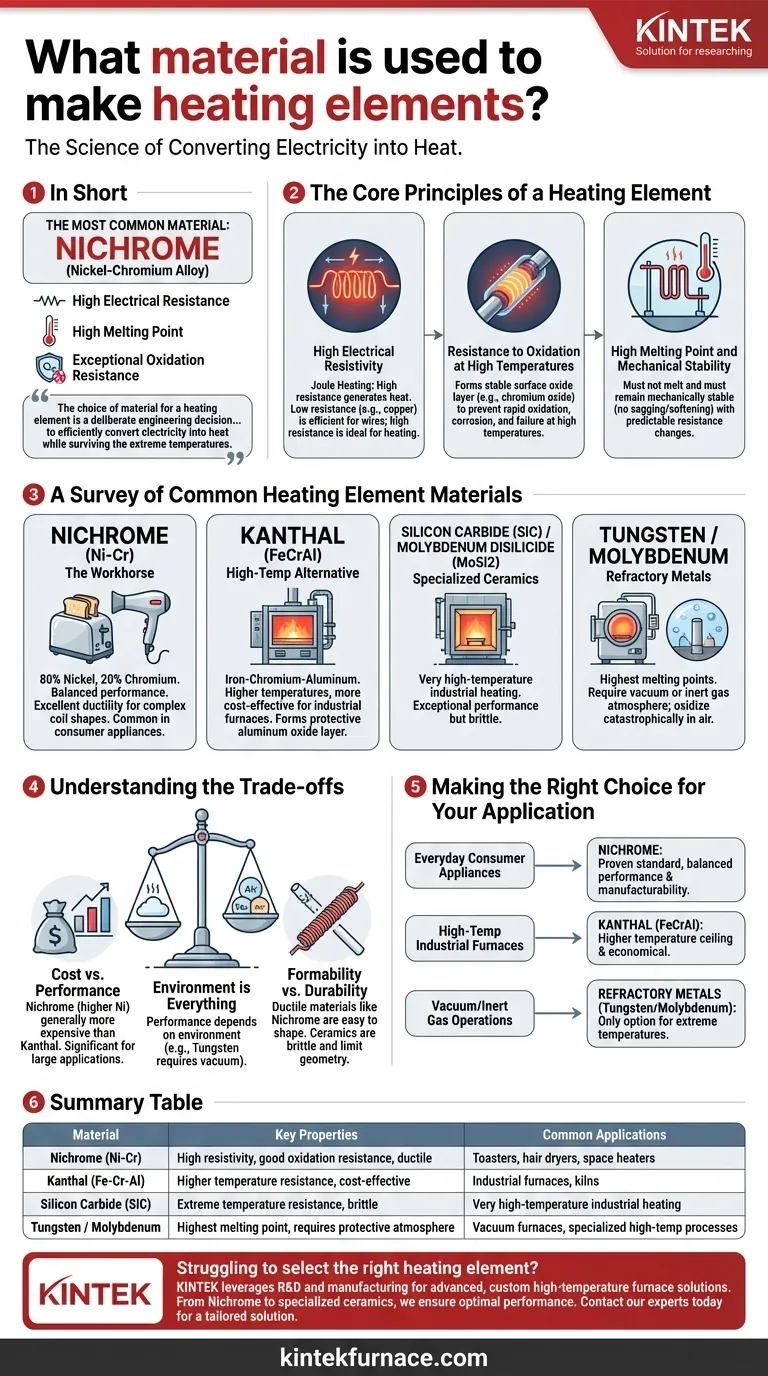
In short, the most common material used for heating elements is Nichrome, an alloy composed primarily of nickel and chromium. This specific alloy is favored because it possesses a unique combination of high electrical resistance, a high melting point, and an exceptional ability to resist oxidation when red-hot.
The choice of material for a heating element is not arbitrary; it is a deliberate engineering decision. The core challenge is finding a substance that can efficiently convert electricity into heat while simultaneously surviving the extreme temperatures and oxidative stress of its own operation.

The Core Principles of a Heating Element
To understand why certain materials are used, we must first understand the fundamental requirements for converting electricity into controlled heat. The ideal material must master three physical challenges.
High Electrical Resistivity
A heating element works by a principle called Joule heating. When electric current flows through a material with resistance, the electrical energy is converted into thermal energy, or heat.
Materials with low resistance, like copper, are excellent for wires because they transfer electricity efficiently with minimal heat loss. For a heating element, the opposite is desired. A high-resistance material is needed to generate heat effectively.
Resistance to Oxidation at High Temperatures
This is the most critical property. Most metals, when heated to hundreds or thousands of degrees in the presence of air, react rapidly with oxygen—they oxidize, corrode, and quickly fail.
The best heating element materials, like Nichrome, form a thin, stable, and adherent layer of oxide on their surface (chromium oxide, in this case). This layer acts as a protective skin, preventing further oxidation and allowing the element to operate for thousands of hours at high temperatures.
High Melting Point and Mechanical Stability
The material must obviously not melt at its operating temperature. It also needs to remain mechanically stable, meaning it shouldn't become overly soft, stretch, or sag in a way that would cause it to fail.
Finally, its resistance should remain relatively constant as its temperature changes. This ensures the heat output is predictable and stable throughout its operating cycle.
A Survey of Common Heating Element Materials
While Nichrome is the most famous, different applications demand different materials, each offering a unique balance of properties.
The Workhorse: Nichrome (Nickel-Chromium)
Composed of roughly 80% nickel and 20% chromium, Nichrome is the default choice for a vast range of consumer and commercial appliances like toasters, hair dryers, and space heaters.
Its popularity stems from its excellent balance of high resistivity, strong resistance to oxidation, and good ductility, which allows it to be easily drawn into wire and formed into coils.
The High-Temp Alternative: Kanthal (FeCrAl)
Kanthal is a trade name for a family of iron-chromium-aluminum alloys. These materials can withstand even higher temperatures than Nichrome and are often a more cost-effective choice for demanding applications.
They are the standard for high-temperature industrial electric furnaces and kilns. Their superior performance comes from the formation of a highly protective aluminum oxide layer.
Specialized Materials for Extreme Conditions
For applications beyond the capabilities of Nichrome or Kanthal, engineers turn to even more exotic materials.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are ceramic materials used in very high-temperature industrial heating, offering exceptional performance but with more brittleness.
- Tungsten and Molybdenum are refractory metals with extremely high melting points. However, they oxidize catastrophically in open air at high temperatures and must be used in a vacuum or a protective, inert gas atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "best" material; there is only the best material for a specific job. The choice always involves balancing competing factors.
Cost vs. Performance
Nichrome, containing a high percentage of nickel, is generally more expensive than Kanthal (FeCrAl) alloys. For a simple appliance, this cost may be negligible, but for a large industrial furnace, the difference can be substantial.
Environment is Everything
A material's performance is entirely dependent on its operating environment. Tungsten is one of the highest-performing heating elements available but is rendered useless in an oxygen-rich environment. Graphite is an excellent conductor but will burn away in air.
Formability vs. Durability
Ductile materials like Nichrome are easy to manufacture into the complex coil shapes needed for many appliances. In contrast, higher-performance alternatives like Kanthal or ceramic elements can be more brittle and difficult to work with, limiting their geometric possibilities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The selection process always begins with defining the operational requirements.
- If your primary focus is everyday consumer appliances: Nichrome is the proven industry standard, offering a superb balance of performance, manufacturability, and reliability.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial furnaces: Kanthal (FeCrAl) alloys provide a higher operating temperature ceiling and are often the more economical choice.
- If your primary focus is operating in a vacuum or inert gas: Refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum are the only viable options for reaching extreme temperatures.
Ultimately, selecting a heating element material is an engineering decision that balances the laws of physics with the demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nichrome (Ni-Cr) | High resistivity, good oxidation resistance, ductile | Toasters, hair dryers, space heaters |
| Kanthal (Fe-Cr-Al) | Higher temperature resistance, cost-effective | Industrial furnaces, kilns |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Extreme temperature resistance, brittle | Very high-temperature industrial heating |
| Tungsten / Molybdenum | Highest melting point, requires protective atmosphere | Vacuum furnaces, specialized high-temp processes |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your high-temperature process?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced, custom high-temperature furnace solutions. Whether your application requires a standard Muffle Furnace or a complex custom CVD/PECVD System, our experts will help you select and integrate the perfect heating element material—from Nichrome to specialized ceramics—to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and efficiency.
Contact our heating experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















